What Does the Future of Bandwidth and Connectivity Hold for Us?
Terms like 3G, 4G, 5G, and LTE are all too common these days. Many people still wonder what they mean!
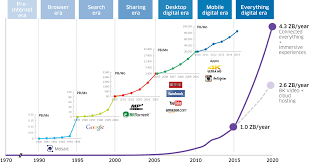
The terms represent the generations of wireless connectivity, hence the “G.” Each subsequent generation is better than the previous one, just as it is with processors, smartphones, computers, etc. Among other things that improve with every generation is bandwidth – the maximum speed at which data can be transferred on your internet connection, also known as internet “speed.” Cellular and Wi-Fi connectivity are the major parts of wireless internet connectivity around the world.
The number of people using mobile devices is increasing, and Wi-Fi usage on mobile devices is also increasing. Internet service providers face a growing demand to provide their users with the capacity and bandwidth they need for voice, text, streaming video, and data transfers. In the early days of the Internet, 1G technology offered a maximum speed of 14.4Kbps. By comparison, 4G internet connectivity offers speeds of up to 100Mbps using Wi-Fi (1 Mbps = 1,000Kbps). The next generation, 5G technology, will bring speeds of up to 1Gbps (1,000 Mbps)! The best thing about this technology will be the efficient use of resources resulting in low-cost and affordable technology with higher reliability.
The networks that will support 5G technology will not be using “old school” copper and fiber technology. Instead, mm-wave (Millimeter-wave) wireless connections will be used, lowering infrastructure costs by big margins and making deployment faster and easier. This new technology will offer benefits not only to the tech companies that provide internet connectivity but also to the e-commerce sector. The days of losing 85% of traffic on slow-loading websites (and today, that is a website that takes more than two seconds to load!) will be gone. 5G technology will make a huge difference for e-commerce, as potential buyers have a more optimal online experience.
Technology to support faster bandwidths is continually being developed. In Florida and the Netherlands, researchers tested a 7-core cable made of glass fiber to increase transmission speeds. They recorded speeds of up to 255Tbps, which is 2,550 faster than the fastest internet connection available from a commercial ISP. The UK has pledged that every house in the nation will soon have an internet connection with speeds of at least 10Mbps. Google Fiber service promises to deliver speeds of at least 10Gbps to its customers.
The future of bandwidth and connectivity is sure to be staggering for those who have watched speeds spiral upward since the 1990s. These lightning-fast speeds are complementing the advent of 3D Printing, as well. Google is advancing driverless cars and these cars will be connected to each other on a network that transfers data at high speeds. The future of cloud computing, increasingly important for all aspects of business, depends heavily on increased internet speeds and bandwidths in the future.
Sources: https://blog.100tb.com/the-future-of-bandwidth-from-5g-to-seven-corehttp://playgroundinc.com/blog/forget-big-data-its-time-to-think-about-big-bandwidth/
RECENT BLOG POSTS